Bitcoin mining is the foundation of the Bitcoin organization. Miners

Bitcoin mining is the foundation of the Bitcoin organization. Miners give security and affirm Bitcoin transactions. Without Bitcoin miners, the system would be assaulted and broken. Bitcoin mining is done by specific computers. The role of miners is to secure the system and to process each Bitcoin transaction. Miners accomplish this by tackling a computational issue which enables them to chain together blocks of transactions (henceforth Bitcoin’s popular “blockchain”). For this, miners are compensated with recently made Bitcoins and transaction expenses.
You May Also Read: Can Blockchain Technology be Hacked?
What is Bitcoin Mining?
There are many aspects of Bitcoin mining, and we’ll go through them here. They are:
- Issuance of new bitcoins
- Affirming transactions
- Security
Mining Is Used to Issue new Bitcoins:
Traditional money forms – like dollar or euro- – are issued by national banks. The national bank can issue new units of cash whenever they feel that it will enhance the economy.
Bitcoin is extraordinary. With Bitcoin, miners are compensated new at regular intervals. The issuance rate is set in the code, so miners can’t deceive the framework or make bitcoins out of nowhere. They need to utilize their figuring capacity to create the new bitcoins.
Miners Confirm Transactions:
Miners incorporate transactions sent on the Bitcoin network in their blocks. A transaction should be marked as secure and completed once it is incorporated into a block. When a transaction has been incorporated into a block, it is formally installed into Bitcoin’s blockchain. More confirmations are better for bigger installments.
Miners Secure the Network:
Miners secure the Bitcoin network by making it hard to attack, change or stop. The more the miners’ mine, the safer the system is. The best way to invert Bitcoin transactions is to have over 51% of the system hash control. Dispersed hash control spread amongst a wide range of miners protects Bitcoin.
You May Also Read: A Beginner’s Guide to Verge Cryptocurrency
What Are Bitcoin Mining Pools?
Mining pools enable miners to get more regular mining payouts. By joining with different miners in a pool, it allows miners to discover blocks, as often as possible.
How do mining pools help?
By joining a mining pool, one offers their hash rate to the pool. Once the pool finds a block, they get a payout in light of the percent of hash rate added to the pool.
How to Mine Bitcoins?
Most of the Bitcoin mining is done in expansive stockrooms where there is cheap electricity. To be honest: most individuals don’t mine bitcoins today.
Steps for Mining Bitcoins
Step 1: Get Bitcoin Mining Hardware:
One won’t have the capacity to mine without an ASIC miner. ASIC miners are particular computers that work with the sole aim of mining bitcoins.
Step 2: Select a Mining Pool:
When one gets their mining equipment, one has to choose a mining pool. Without a mining pool, one can get a mining payout on the off chance that he/she found a block alone. This is called solo mining.
Step 3: Get Bitcoin Mining Software:
Bitcoin mining programming is the means by which one can guide mining equipment into their coveted mining pool. One needs the product to point their hash rate at the pool.
The most effective method to Mine Bitcoins on Android or iOS
One can mine bitcoins on any Android device. Using an application like Crypto Miner or EasyMiner one can mine bitcoins or some other coin. But the earnings through the mobile platform will be less than a penny in a year.
You May Also Read: Ethereum Classic Mining
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
This pictorial representation is useful to understand working:
1) Spending: Suppose the Green client needs to get a few products from the Red client. Green sends one bitcoin to Red.
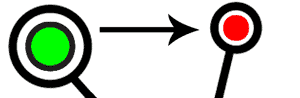
2) Announcement: Green’s wallet reports a one bitcoin installment to Red’s wallet. This data, known as the transaction, is communicated to the same number of Full Nodes as an associate with Green’s wallet – usually 8. A full node is an uncommon transaction handing-off wallet which keeps up a present duplicate of the whole blockchain.
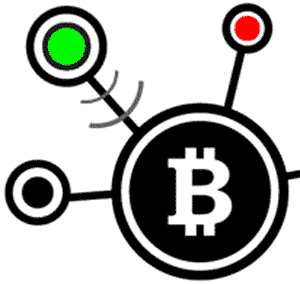
3) Propagation: Full Nodes at that point check Green’s expenditure against other pending transaction. If there are no conflicts (e.g., Green didn’t attempt to cheat by sending precisely the same to Red and a third client), full nodes communicate the transaction over the Bitcoin organize. Now, the transaction has not yet entered the Blockchain. Red would risk by sending any products to Green before the transaction is confirmed. So how do transactions get affirmed? This is the place. Miners enter the scene.
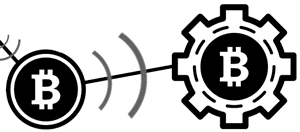
4) Processing by Miners: Miners, like full hubs, keep up a total duplicate of the blockchain and screen the system for recently reported transactions. Green’s transaction may, in reality, achieve a miner straightforwardly, without being handed-off through full nodes. In either case, a miner at that point performs work trying to fit all new, legitimate transactions into the present block.
Miners race each other to finish the work, which is to “bundle” the present block with the goal that it’s satisfactory to whatever is left of the system. Worthy blocks incorporate an answer for a Proof of Work computational issue, known as a hash. The more registering power a miner controls, the higher their hash rate and the more noteworthy their chances of explaining the present block.
The SHA-256 algorithm is used by Bitcoin to deliver hashcode:
“6afc21238f2d33e24e168195888721dd5ace05d76196671d6739789af92201ed”
Thus, a hash is an approach to confirm any measure of information is exact. To explain a block, miners alter non-transaction information in the present block to such an extent that their hash result starts with a specific number (as per the current difficulty, secured beneath) of zeroes.

5) Blockchain Confirmation: The primary miner to solve the block containing Green’s installment to Red reports the recently understood block to the system. If other full nodes concur the block is legitimate, the new block is added to the blockchain, and the whole procedure starts once again. Once recorded in the blockchain, Green’s installment goes from pending to affirmed status.
Red may now think about sending the merchandise to Green. Notwithstanding, the all the more new blocks are layered on the one containing Green’s installment, the harder to turn around that transaction moves toward becoming.
Here Are A Few Other Articles For You To Read Next:

