It’s been a while that there has been much debate
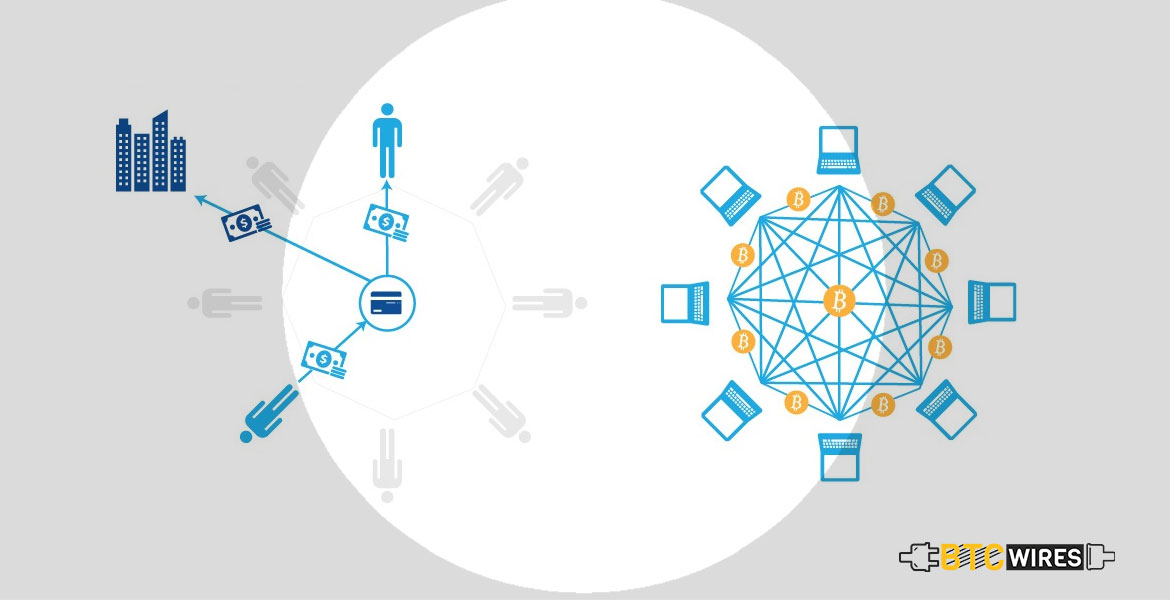
It’s been a while that there has been much debate about the potential advantages of blockchain technology to improve the payments sector – international payments particularly.
It’s a kind of business where different parties need to reach a particular consensus to give direction to the payments, perform currency conversions as well as deploy and manage the liquidity in the different jurisdictions.
One of the primary problems blockchain can tackle is the enhanced complexity of payments networks, owing to the disintegration of the financial industry itself, that makes it impractical for the individual banks to deal directly with other banks across the world.
For instance, the point a bank gets a payment instruction from a particular client, then it needs to get a correspondent bank that wants to take the client’s fund and terminate the payment at the receiving bank. And to do that, the correspondent bank needs to have a Nostro or Vostro bank account with the receiving bank, ideally with adequate pre-funded liquidity for completing the payment on the client’s behalf.
When this happens, the receiving bank gets no way to clarify that the incoming transfer from the correspondent bank corresponds to the original client sending the money. That is the reason, a SWIFT message from the sender is required so that the receiving bank can easily comprehend the purpose of the incoming transaction, do the due diligence properly, and inform the receiver of the funds.
All the parties which are involved in the transaction have different ledgers, meaning that they don’t share the truth, and the coordination between all these parties is, of course, slow and error-prone, many times depending on manual interventions by back-office teams. Moreover, someone needs to perform currency conversion at an end, and different parties need to manage liquidity levels at Nostro or Vostro bank accounts, involving to settle against central bank accounts too.
Blockchain Has The Proper Solution
Blockchain promises to provide that single version of the truth in the precise manner that is missing in the discussion above.
Sure, a true, smart contract-enabled blockchain offers a single ledger as well as transactional engine where balances can be maintained as well as transacted upon and where payments can reside as single, common digital objects making the reconciliation and messaging unnecessary.
Using smart contracts, various parties can not just register the tokenized funds and payments, but also set in stone rules applying to all the aspects of the end-to-end payments processes, exterminating errors as well as misunderstandings, increasing audibility & transparency, and reducing fraud and cyber attacks.
What Would Be The Result Then?
Unlike our centralized system, everything would be on the same ledger, on the same computational engine, with the same smart contracts for all, with no possibility of errors or tampering.
Presently, most of the decentralized solutions being proposed focus on improving the payment processes. It’s being done either by digitizing the messaging layer or by eliminating it with the creation of single, digital representation of payments to enforce the transactions on a proprietary ledger that are linked to one another with a kind of inter-ledger protocol. Indeed, this is a significant improvement on today’s message-drive payments processes.
Blockchain’s 3 Promises
1. It will accelerate the international payment processing services
Some blockchain-based payment processing services already exist for B2B transactions, whereas the others are expected to launch by the end of 2018. Probably, the biggest emerging trend is the use of distributed-ledger technologies unrelated to Bitcoin, like Ethereum and Ripple. In Japan, a consortium of banks planned to go live in the Spring of 2017 with a blockchain-based payment processing services which supported the real-time domestic as well as cross-border payments at lower cost versus traditional services.
Many existing blockchain-based B2B payment processing services are based on Bitcoin. A few of these are designed for the relatively small subset of the companies trading directly in Bitcoin. But other payment processing solutions confronts a much larger audience by utilizing Bitcoin distributed ledger to transfer the payments in conventional currencies, which enables them to bypass the current banking infrastructure, with the objective of speeding up the payment and reducing the additional cost. The provider changes the payer’s local currency into Bitcoin, then changes the Bitcoin into the receiver’s local currency, usually delivering the international payments within 1 to 3 days.
Santander has become the first UK Bank that has introduced the blockchain technology for international payments.
2. It will lower the cost of trade financing
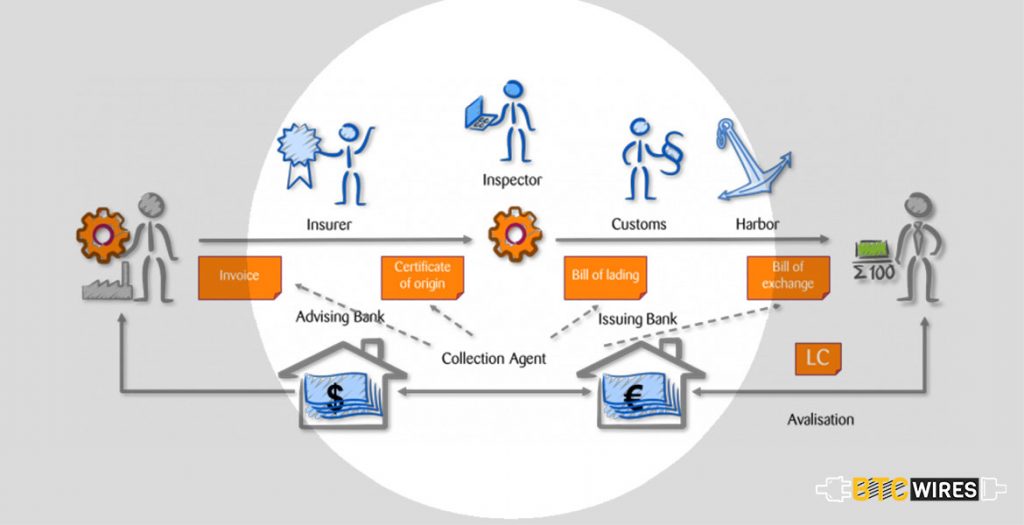
A number of initiatives are concentrating on applying blockchain with an aim to speed and reduce the cost of trade finance. Some people consider this as a ripe for disruption as it presently involves, time-consuming, costly and paper-based manual processes. In a recent proof of concept, Brighann Cotton and Wells Fargo undertook what was believed to be the first live blockchain-based transaction globally that involves two banks. The transaction involved a collaborative workflow in order to track and pay for the shipment of cotton between two units in China and Texas.
In spite of the potential benefits, some people believe that it may take time for the blockchain to trade finance solutions to become prevalent. A Boston Consulting Group report evaluates that technologies incorporating blockchain could reduce the compliance and operational costs by 10 to 15%.
3. Contracts That Execute On Their Own

When it comes to trade finance applications, a key capability of blockchain technology is smart contracts. These are self-executing programs stored on the distributed ledger which automatically execute payments at the point when specific conditions are met.
Conclusion
The correspondent blockchain applicataion in banking system has served its users from the time immemorial. But the expectations of money senders and receivers have changed greatly over the period of time, requiring new approaches which are more economical, secure, rapid, transparent and convenient. The blockchain is what solves all the problem like a pro. It is meant to improve the payment processing and is doing quite well.

